Clinical Trial Summary Report
C. Thomas Dow, M.D.1
Objective. This study was undertaken to determine if a self-directed, computer-based response to presented stimuli (Opternative exam) can generate a refractive outcome that approximates the results of a manifest refraction as determined by experienced eye care professionals (Manifest exam).
Method. The results from sixty eyes of thirty consecutive subjects meeting inclusion/exclusion criteria2 who successfully completed the Opternative exam were analyzed for comparison to the refractive results of a Manifest exam in a double blind fashion. Subjects were given trial frames at the completion of both exams in order to evaluate their vision in both an objective (LogMAR acuity) and subjective fashion (survey quesionnaire). The questionnaire contained a 10 point visual satisfaction ranking question, where 0 was blind and 10 was perfect vision. The questionnaire also contained a confidence based question to determine how confident the subjects were after wearing the respective prescriptions. The 10 point confidence questionnaire had a rating scale of 0 being not confident, and 10 being extremely confident.
Results. Visual satisfaction rating, as determined by survey, measured symmetrically high for both tests. The Opternative exam received an average visual satisfaction rating of 8.633 out of 10 (with 10 being the best vision), while the Manifest exam received an average visual satisfaction rating of 8.917. In addition, the Opternative exam received an average confidence rating of 8.700 out of 10 (with 10 being the most confident), while the Manifest exam received an average confidence rating of 8.967. 42/60 (70%) eyes had a spherical equivalent difference of 0.25 diopter or less; while 54/60 (90%) eyes had a spherical equivalent difference of 0.55 diopter or less. Best corrected visual acuity average measurements determined with trial frame lenses from both of the two refractive modalities produced results better than 20/20: 20/15.9 LogMAR (Opternative); 20/14.9 LogMAR (Manifest). Spherical equivalence (SE) correlation was found to be very high, with an r value of 0.925, and 88% of the prescriptions were within 0.55D of one another.
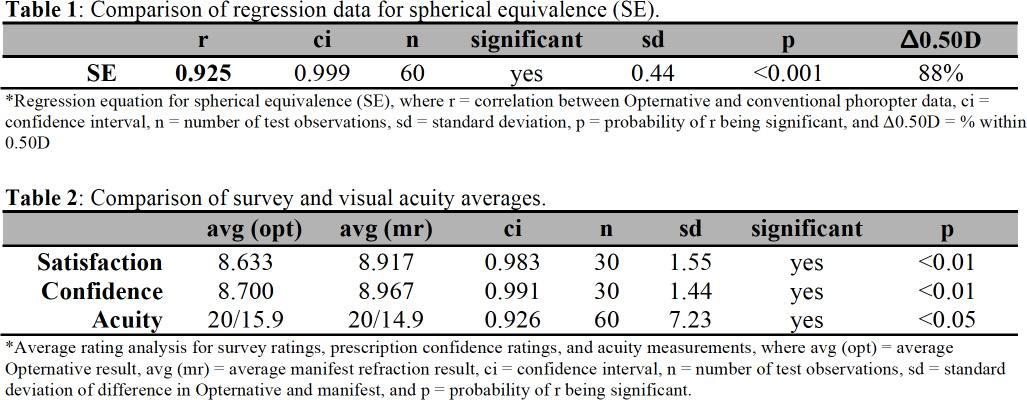
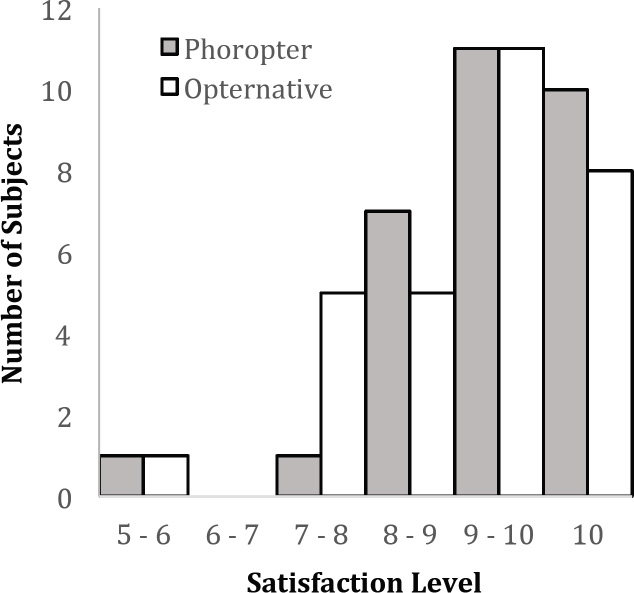
Figure 1: Visual satisfaction ratings from the Opternative exam and conventional phoropter based exam.
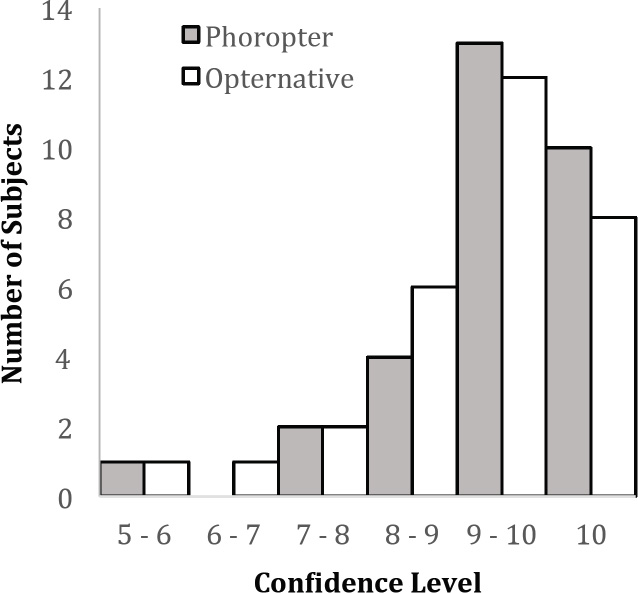
Figure 2: Subject confidence ratings from the Opternative exam and conventional phoropter based exam.
Figure 3: Visual acuity LogMAR results from subjects who took the Opternative exam and conventional phoropter based exam.
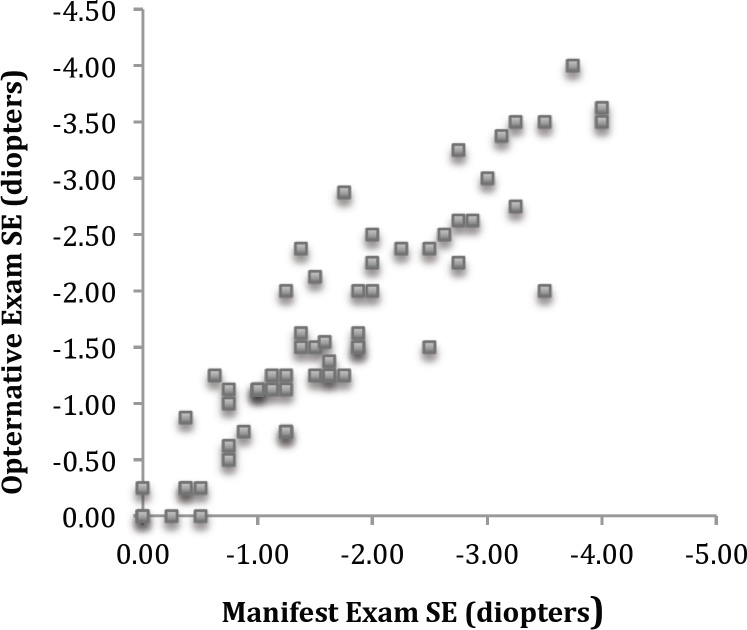
Figure 4: Correlation between Opternative exam SE and conventional phoropter based exam SE.
Discussion. The preliminary evaluation of the Opternative digital refraction system shows strong refractive correlation with the traditional manifest exam. In accordance with the study protocols the Opternative digital exam was placed purposely at a disadvantage, generating prescriptions from scratch, versus the Manifest exam that had assistance from prior prescriptions. The exam not only shows a high visual acuity outcome from prescriptions generated from the Opternative examination, but also high confidence level from patients receiving an Opternative prescription; moreover, survey shows the Opternative exam to provide a satisfactory interactive experience.
1 Chippewa Valley Eye Clinic, Eau Claire, Wisconsin and McPherson Eye Research Institute, Madison, Wisconsin.
2 18-40 year olds with no ocular or systemic disease, myopia up to -4.00, astigmatism up to -2.00
Get In Touch


